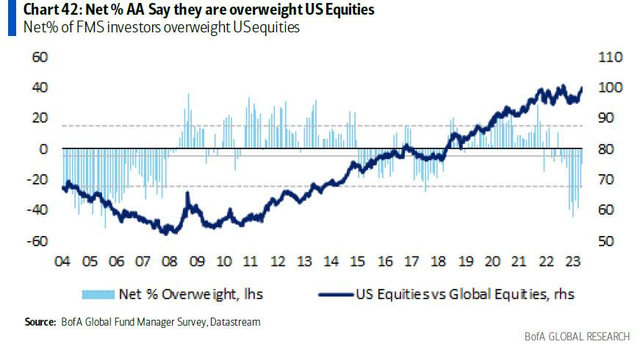
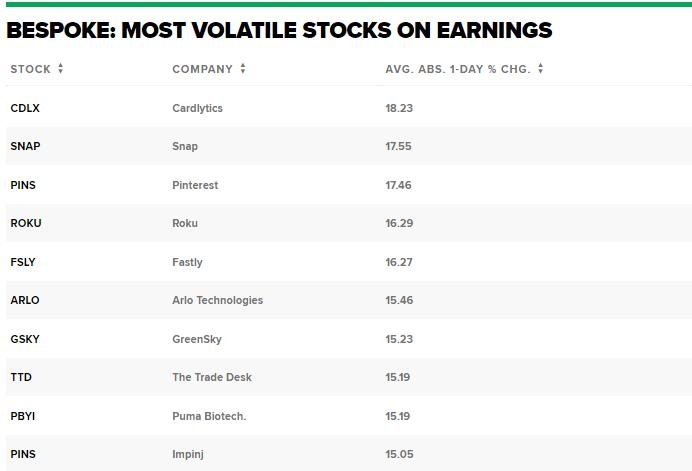
Investing in stocks can be a lucrative venture, but it's crucial for tax residents to understand the rules and regulations before diving in. If you're a tax resident looking to invest in the US stock market, this guide will provide you with essential information to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Tax Residents in the US
Firstly, it's important to clarify what it means to be a tax resident in the US. Generally, individuals who live in the US for more than 183 days in a given year are considered tax residents. This includes citizens, green card holders, and those with substantial presence in the country.
Investing in Stocks for Tax Residents
Once you've established your tax residency status, you can proceed to invest in stocks. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Brokerage Accounts
To invest in stocks, you'll need a brokerage account. This account allows you to buy and sell stocks, bonds, and other securities. There are various types of brokerage accounts available, including:
- Individual brokerage accounts: Ideal for single investors.
- Joint brokerage accounts: Suitable for married couples or partners.
- IRA accounts: Retirement accounts that offer tax advantages.
2. Tax Implications
When investing in stocks, it's important to understand the tax implications. Here are some key points to consider:
- Capital gains tax: If you sell a stock for a profit, you'll be subject to capital gains tax. The rate depends on how long you held the stock. Short-term gains (less than a year) are taxed as ordinary income, while long-term gains (more than a year) are taxed at a lower rate.
- Dividend tax: If you receive dividends from your stocks, you'll be subject to dividend tax. The rate depends on your income level and the type of dividend (qualified or non-qualified).
- Tax reporting: You must report your stock investments on your tax return using Form 8949 and Schedule D.
3. Investment Strategies
As a tax resident, you can adopt various investment strategies to maximize your returns. Here are some popular strategies:
- Dividend investing: Investing in companies that pay regular dividends can provide a steady income stream.
- Growth investing: Investing in companies with high growth potential can lead to significant capital gains.
- Value investing: Investing in undervalued companies can provide attractive returns over the long term.
4. Case Studies
Let's consider a few case studies to illustrate the tax implications of stock investments:
- John invested in a stock and held it for less than a year. He sold the stock for a profit of
10,000. John will be taxed on the 10,000 as ordinary income. - Mary invested in a stock and held it for more than a year. She sold the stock for a profit of
10,000. Mary will be taxed on the 10,000 at the long-term capital gains rate, which is lower than the ordinary income rate. - James received a dividend of
1,000 from a company. Since James is in the 25% tax bracket, he will pay 250 in dividend tax.
Conclusion
Investing in stocks can be a rewarding endeavor for tax residents in the US. By understanding the rules and regulations, you can make informed decisions and maximize your returns. Remember to consider the tax implications and adopt a suitable investment strategy to achieve your financial goals.
us flag stock
 spv stock-Start small, grow steady, and turn your U.S. market dreams into tangible returns today.Democratize your U.S. stock investing journey—no fancy degrees or huge capital required.....
spv stock-Start small, grow steady, and turn your U.S. market dreams into tangible returns today.Democratize your U.S. stock investing journey—no fancy degrees or huge capital required.....